What’s new for February 2024?
We have a lot of celestial astronomical discoveries.
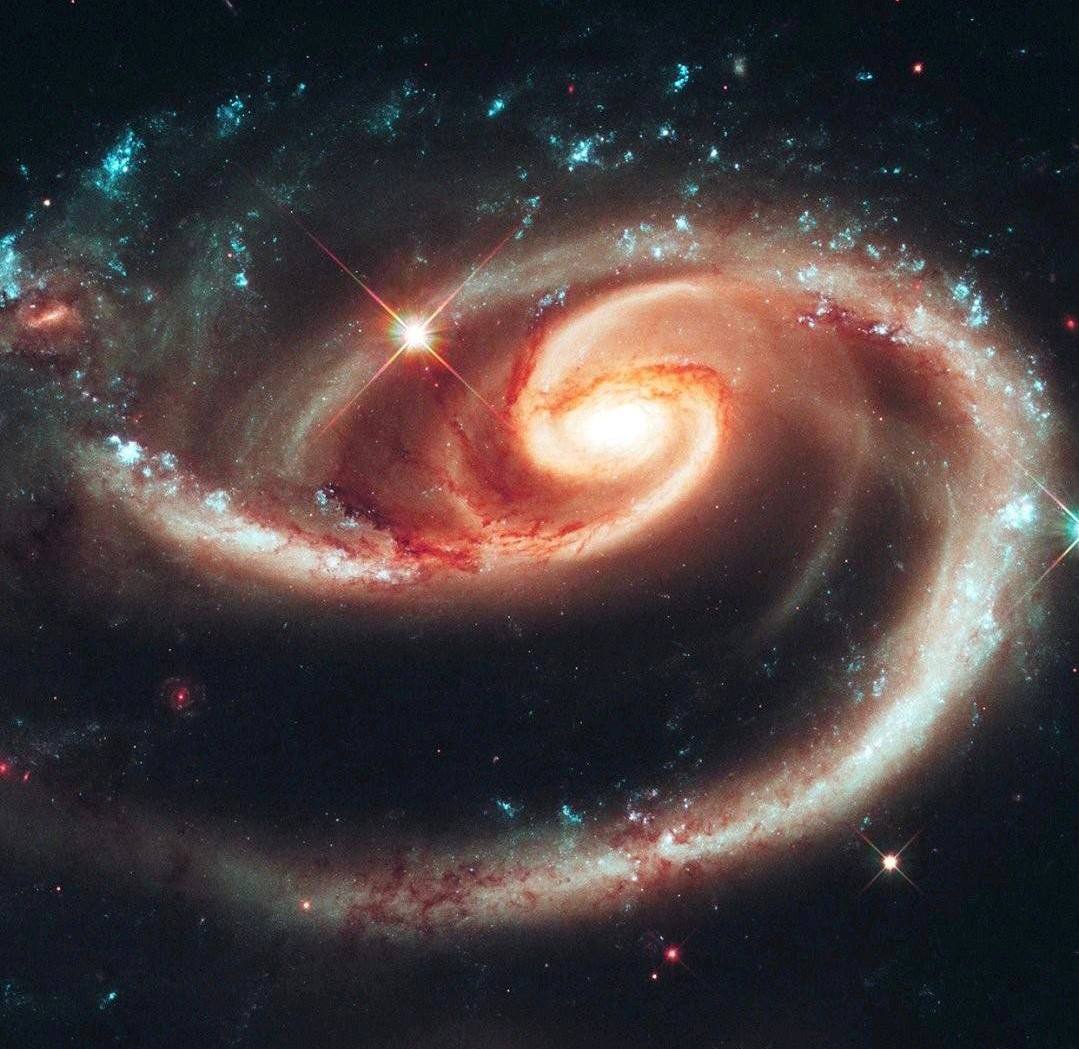
Venus and Mars will become a special couple, Jupiter and the Moon will play a romantic scene, and M81, also known as the “Bode Galaxy,” asks for caution.
M81 is a spiral galaxy, similar to our Chumatsky Shlyakh, but only a little less, one of the brightest in the night sky. Vaughn is located approximately 11.8 million light rocks away from us, which means that light, as we know, has risen in price in space by more than 11 million rocks, before reaching our eyes….
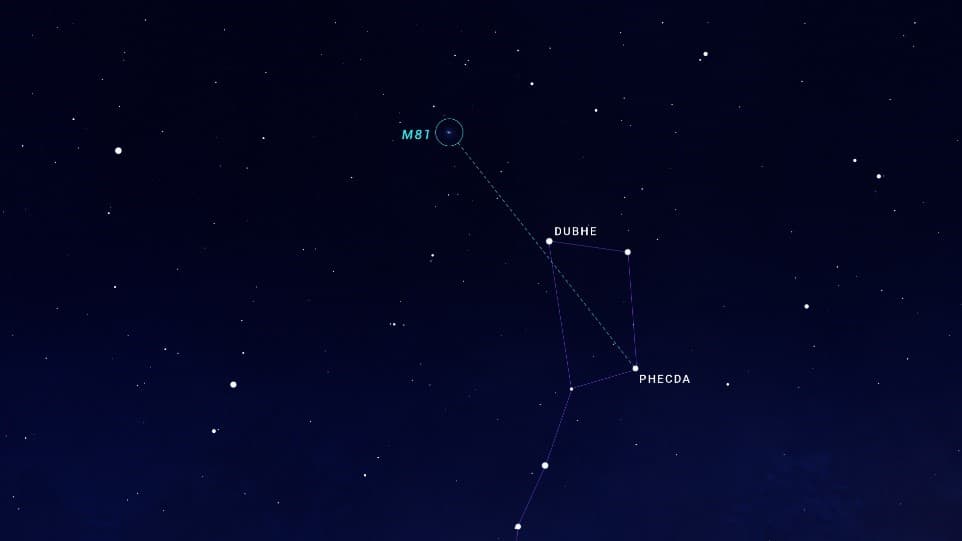
Finding M81 is not difficult. Take the Big Dipper (or the Plow) as a guide. Start at the star Dubhe and extend the line to Thekda, the star at the opposite end of the Ursa Major, twice as long. Point your telescope or binoculars at this area and you’ll find M81.
In 1774, the astronomer Johann Bode discovered this object, which later received his name and is commonly known as the Bode Galaxy. It was initially classified as a nebula or a faint, faint formation. However, only in the 1920s, thanks to the work of Edwin Hubble, many such faint objects began to be considered as separate galaxies located outside the Milky Way and extremely distant from our planet.
Venus still impresses with its brightness in the morning sky, but the end of February is destined to disappear in the light of the sunrise. The resumption of Venus as an evening object can be enjoyed in July.
Regarding observations in February
- Full Moon – Venus will be visible in the eastern sky until sunrise, but its brightness will decrease each day.
- The whole month – Mars will appear in the pre-dawn sky. Although it will not be very bright, its growth should be monitored in the coming months.
- February 6 – Venus and the crescent moon can be seen in the east when the sky begins to lighten.
- February 9 – new moon.
- February 14 – Look for a crescent moon with Jupiter in the southwest after sunset.
- February 22-28 – The closest approach of Mars and Venus is expected if you have an unobstructed view of the southeastern horizon.
- February 24 – full moon.
Here are the phases of the moon for February 2024




